Planning Vs Performance Materiality
Auditing standards dictate that the tolerable misstatement level should never exceed performance materiality. While Section 320 requires a distinction between performance materiality and tolerable.

Distribution Of Performance Materiality Based On Survey Of Audited Download Scientific Diagram
Your overall planning materiality applies to the financial statements but your performance materiality applies to your testing sample.

Planning vs performance materiality. These smaller items could be material when aggregated so the performance materiality level is set to accommodate them. MATERIALITY IN PLANNING AND PERFORMING AN AUDIT ISA 320 316 Objective 8. Always tie the materiality level chosen for the audit back to the users of the FS.
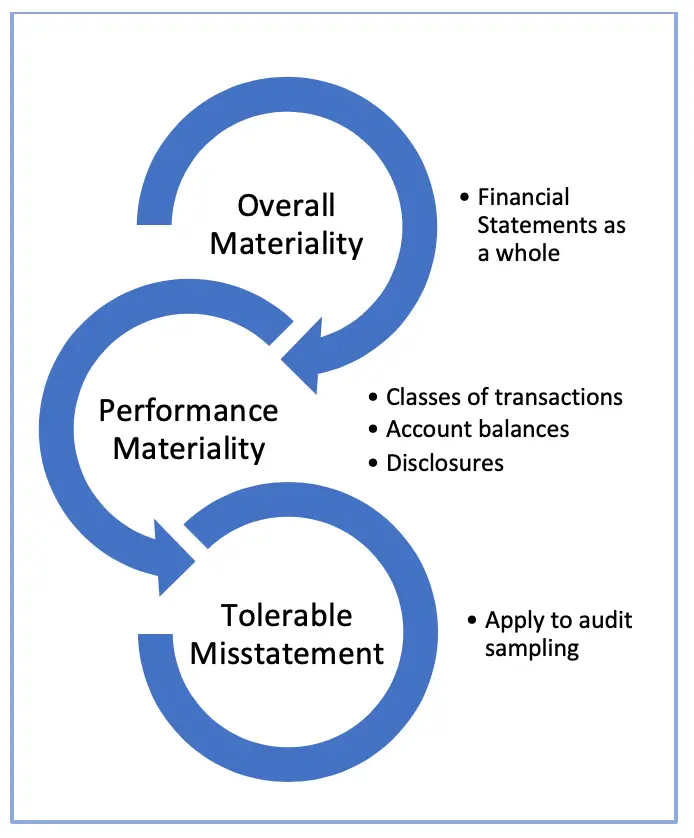
If applicable performance materiality also refers to the amount or amounts set by the auditor at less than the materiality level or levels for particular classes of transactions account balances or disclosures. I Planning stage The concept of materiality is used in determining the nature timing and extent of further audit procedures. Auditors set the materiality for the financial statements as a whole referred to in this guide as overall materiality at the planning stage.
The tolerable Misstatement threshold was set at 90 since the perceived risk was relatively low. The financial statements as a whole. Requirements Determining Materiality and Performance Materiality When Planning the Audit 10.
Performance materiality is an amount less than the level of overall materiality and is reduced in order to allow for the risk that there may be several smaller errors or omissions that have not been identified by the auditor. Previously used terms such as planning materiality and tolerable misstatement have been changed by AU-C Section 320 to materiality and performance materiality respectively. There are several factors that may affect how much this threshold including the level of assurance materiality performance materiality etc.
Explain how setting a lower materiality level affects the number of items that are material and affects the decisions about the nature extent and timing of the audit procedures. Ii Reporting stage The materiality concept is used in evaluating the effect of uncorrected misstatements if any on the financial statements and in forming the opinion in the auditors report. Materiality Performance Materiality Error Threshold HAW video preview included in the Audit Planning section is now available for learn more about HAW.
Planning materiality must be larger than performance materiality. Performance materiality enables the auditor to respond to specific risk assessments without changing the planning materiality and to reduce to an appropriately low level the probability that the aggregate of uncorrected misstatements exceeding planning materiality. The objective of the auditor is to apply the concept of materiality appropriately in planning and performing the audit.
Relationship of Planning and Performance Materiality to Sampling Concepts. Explain the relationship between planning materiality and performance materiality. Similarly performance materiality relating to a materiality level determined for a particular class of transactions account balance or disclosure is set to reduce to an appropriately low level the probability that the aggregate of uncorrected and undetected misstatements in that particular class of transactions account balance or disclosure exceeds the materiality level.
Materiality vs Performance Materiality While materiality and performance materiality are closely related to each other there are still some differences between them. One single amount for the entire Financial Statement. For purposes of the ISAs performance materiality means the amount or amounts.
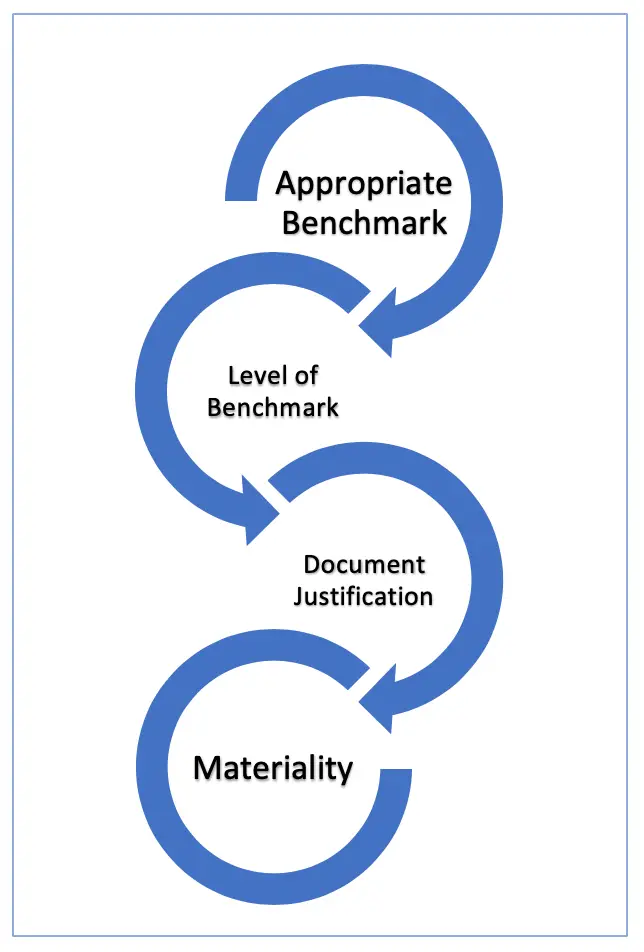
1No Benchmark Auditors assessment 2. Use to judge important account balance and class of transaction. The auditor is to apply the concept of materiality in planning and performing the audit.
This is because the planning materiality is the materiality amount to financial statements and performance materiality is the possible misstatements that expected to have happened in the financial statements alone or. Planning materiality is an amount set by auditors during the audit planning stage. Home Questions Clearly trivial vs performance Materiality 0 Vote Up Vote Down Shubham asked 4 years ago Question Tags.
Different amounts for different ledgersaccounts. For example your materiality is 10k youd apply that to the overall widget expense account. 11A15 Planning the audit solely to detect individual material misstate-ments overlooks the fact that the aggregate of individually immaterial mis-statementsmaycausethefinancialstatementstobemateriallymisstatedand leavesnomarginforpossibleundetectedmisstatementsPerformancemateri-.
SA 450 7 Answers 0 Vote Up Vote Down Ravi Staff answered 4 years ago clearly trivial means very small 1 to 5 of materiality value such misstatements below this amount should be ignored. Based on previous year records and industry standards auditors decided to set the planning materiality at 1 of the revenue. Misstatements are considered to be material if they individually or in the aggregate could reasonably be expected to influence the economic decisions of users.
Performance materiality is set at lower amount than planning materiality. Performance materiality applied to sampling applications is now termed tolerable misstatement. The concept of planning materiality was introduced in SAS 39 Audit Sampling in 1981 and expanded in SAS 47Although neither SAS 39 nor SAS 47 discussed it in considerable depth it was covered further in Appendix L of the 2006 audit guide Assessing and Responding to Risk in a Financial.
Based on this the planning materiality for all the line items in the financial statements was set at 2500. Individual balance in an individual account. The primary purpose for setting overall materiality when planning the audit is that it is used to identify performance materiality which is needed for example to help auditors design their.
First of all materiality refers to the idea that a single misstatement in the financial statements of a business can affect the ability of users to make economic decisions based on those financial. Planning materiality is the materiality of the financial statements as a whole while Performance is generally a percentage of Planning based on risk and qualitative factors.
Materiality And Tolerable Misstatement Accountinguide

Planning Aicpa Auditing Standards State Three Main Reasons

Component Materiality For Group Audits

Component Materiality For Group Audits
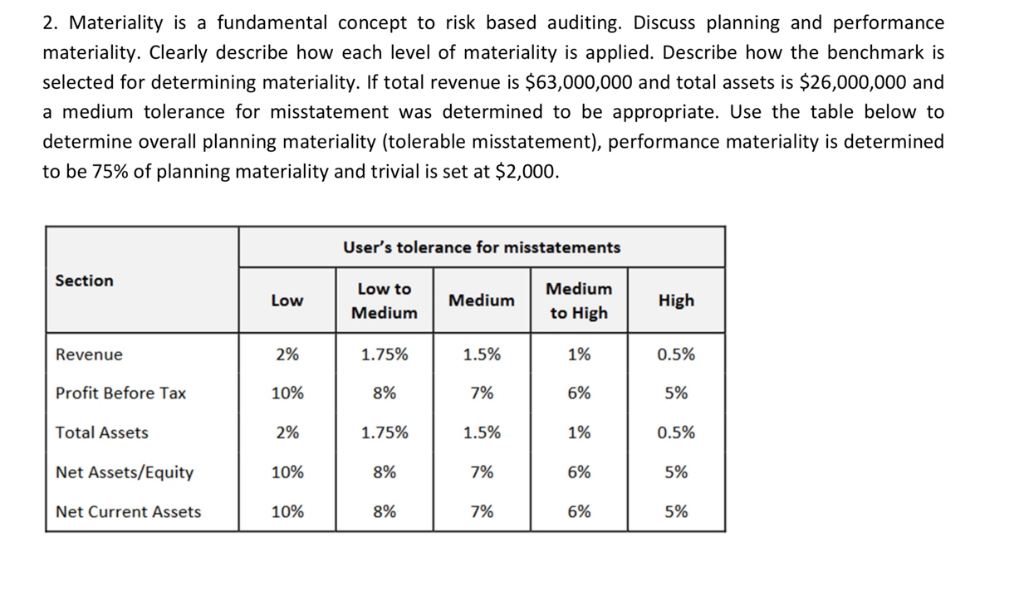
Solved 2 Materiality Is A Fundamental Concept To Risk Based Chegg Com
Solution Ling Consider In Setting Performance Materiality

Difference Between Materiality And Performance Materiality Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Determine Materiality In Audit Which Benchmark To Use Accountinguide

Chapter 7 Assessing Specific Business Risks And Materiality Ppt Video Online Download

How To Align A Robust Materiality Assessment With Corporate Strategy

Ppt Part Two Audit Objectives Planning The Audit Materiality Powerpoint Presentation Id 7011719

Difference Between Materiality And Performance Materiality Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Qualitative Considerations For Allocating Materiality To Components In A Group Audit

Audit Planning Types Of Audit Tests And Materiality Ppt Download
Posting Komentar untuk "Planning Vs Performance Materiality"